Abstract
Introduction
In the last decade, the incorporation of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies (MoAb) (rituximab, obinutuzumab), bendamustine, B-cell receptor inhibitors (ibrutinib) and Bcl-2 antagonists (venetoclax) have changed the paradigm of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treatment, improving overall survival (OS).
Methods
We conducted a retrospective observational study of patients diagnosed with CLL between 2003 and 2016 at our center to evaluate: i) the influence of date of diagnosis, before or after 2010; ii) having received new drugs (MoAb or target therapies) in first line or not.
Results
A total of 182 patients were evaluated: 104 men (57%) and 78 women (43%); median age 74 years (39 - 97), 132 patients were >65 years (72.5%). At diagnosis, 135 (74%), 19 (10%), 15 (8%), 4 (2%) and 9 (5%) were diagnosed as stages 0, I, II, II, III and IV of the Rai classification. While 154 (84%) 15 (8%) and 14 (8%) were classified as Binet's stages A, B and C. Regarding the presence of comorbidities, the median CIRS scale score was 4 (0 - 15). 71 patients (39%) were diagnosed before 2010 and 111 (61%) from 2010 onwards.
With a median follow-up of 76 months (range, 20-212), 77/182 (42%) patients had received ≥1 line(s) of treatment: 1: 53%, 2: 26%, 3: 8%, ≥4: 13%. 20 patients (26%) received the first line of treatment before 2010, and 56 (74%) from 2010 onwards. Half of the patients received new drugs in 1st line (n=39), 92% of them from 2010 onwards. 32 patients (41.5%) achieved complete response after 1st line, and 24 (31%) at least a partial response.
The median OS of patients diagnosed before 2010 was 66 months (35.32 - 96.68) vs 143 months (95% CI 90.5 - 195.5) (p=0.032) as of 2010. In those ≤ 65 years median OS has not been reached, being 80.5% at 10 years: 65% for those diagnosed before 2010 and 97% after 2010, p=0.036. The median OS of patients > 65 years was 6 years (95% CI 4.17 - 7.83), and increased from 82 months for those diagnosed before 2010, to 110 months in those diagnosed after 2010, p=0.744.
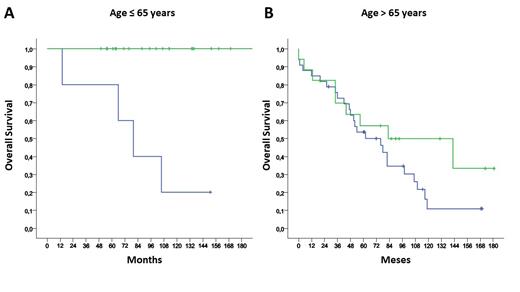
Patients treated with new drugs in 1st line increased the median OS from 76 months and 13% at 10 years to a median not reached and OS of 77% at 10 years, p=0.000. This difference was more evident in those ≤ 65 years: 20% vs 100% at 10 years (p=0.012), while it was not statistically significant for those > 65 years (11% vs 50% at 10 years, p=0.181) (Figure 1). However, in a multivariate model including age, sex, CIRS>6 and year of diagnosis (before or after 2010), treatment with new drugs retained statistical significance (HR 0.414; 95% CI 0.183 - 0.935) along with age ≤ 65 years (HR 0.256; 95% CI 0.085 - 0.771) and CIRS ≤ 6 (HR 0.247; 95% CI 0.111 - 0.551).
Conclusions
In our experience, the introduction of new drugs in the first line has led to an increase in OS, especially in young patients.
Gonzalez-Lopez: Grifols: Other: Advisory board honoraria; Sobi: Other: Advisory board honoraria; Amgen: Other: Advisory board and speakers honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Other: Advisoryboard and speakers honoraria, Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal